Acetoacetylated Resins
Properties and Applications
Acetoacetylated oligomers and polymers are highly reactive, low viscous functional resin modifiers having excellent compatibility with a wide range of resins. They are typically formed by the reaction of hydroxy functional resins with methyl acetoacetate (transesterification). The replacement of the hydroxyl groups with the less polar diketone reduces the viscosity and permits higher solids of solvent-borne products.
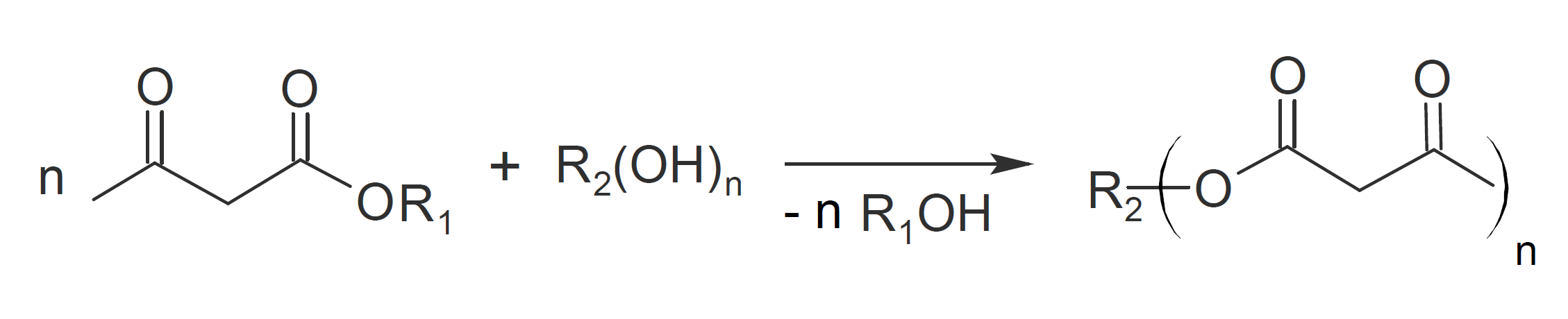
Acetoacetylated resins can undergo a variety of (crosslinking) reactions. The resins have two reactive sites: the active methylene groups and the two ketone carbonyl groups. The active hydrogen on the methylene will react with melamines and isocyanates at room temperature or and with blocked isocyantes and methylated melamines at elevated temperatures, while the ketone groups readily react with amines and hydrazides at ambient conditions.1-3
Acetoacetylated reactive resins are mainly used as modifiers and cross-linking agents in both solventborne and solventless products such as paints, coatings, enamels, adhesives and inks. They allow for low temperature cure and drying, higher solid content and thus reduce energy consumption.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1A fully methylated melamine requires a temperature of about 150°C and an acid catalyst. (Eastman AAEM brochure, 2013)
2The reaction with blocked isocyanates and methylated melamine is slower and allows for longer pot-life and the formulation of 2k systems.
3Eastman™ AAEM - Acetoacetyl Chemistry, Eastman Chemical Company, 2013